39 labels in assembly language examples
PDF Assembly Language Programming - UTEP - Labels are symbols - Labels must begin in column 1. - A label can optionally be followed by a colon - The value of a label is the current value of the Location Counter (address within program) - A label on a line by itself is a valid statement - Labels used locally within a file must be unique. Adapted from notes from BYU ECE124 5 Assembler User Guide: Labels - Keil 7.6 Labels A label is a symbol that represents the memory address of an instruction or data. The address can be PC-relative, register-relative, or absolute. Labels are local to the source file unless you make them global using the EXPORT directive.
What Is Assembly Language (With an Example) | Indeed.com In this example, "1:" is the label, which lets the computer know where to begin the operation. The "MOV" and "ADD" is the mnemonic command to move the number 3 into a part of the computer processor where it can function as a variable. "EAX," "EBX" and "ECX" are the variables. The first line of code loads 3 into the register "eax."
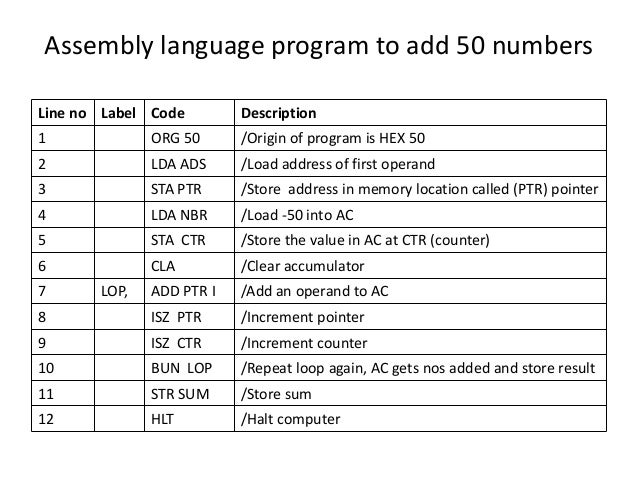
Labels in assembly language examples
Label (computer science) - Wikipedia In assembly language labels can be used anywhere an address can (for example, as the operand of a JMP or MOV instruction). Also in Pascal and its derived variations. Some languages, such as Fortran and BASIC, support numeric labels. Labels are also used to identify an entry point into a compiled sequence of statements (e.g., during debugging ). retro computing - How do labels execute in Assembly ... A label is just a name for a location in your program. Labels are only used during assembly and do not generate any code. They do not "contain" anything or "execute" in any way. A function in assembly typically starts with a label, so that you can refer to the function by its name instead of having to figure out the address yourself ... 8051 - "Label" in Assembly language - Stack Overflow Label is not bypassed. If you take a look at working of a loop then u will see that first DJNZ decrements the value of register then if the result is non zero it executes the label. In 1st example, starting from above: 1) A gets zero, then. 2) R2 gets 10, then. 3) A gets 25, then. 4) DJNZ decrements the value of R2 making it 9 and since the ...
Labels in assembly language examples. pic microcontroller assembly language programming examples For example MOVLW is an Opcode. Labels. A label is an identifier used to represent a line in code or section of a program. Goto statements can be used in conjunction with a Label to jump to the execution of code identified by the particular label. See Task 1 code for example. ... pic microcontroller assembly language examples 6. PDF Assembly Language: Overview - Princeton University • Assembly language! • In between high-level language and machine code! • Programming the "bare metal" of the hardware! • Loading and storing data, arithmetic and logic operations, checking results, and changing control flow! • To get more familiar with IA-32 assembly! • Read more assembly-language examples! 2 Assembly Language Programming - University of New Mexico In an assembly language program, a label is simply a name for an address. For example, given the declarations shown in Example 2.1, ``x'' is a name for the address of a memory location that was initialized to 23. On the SPARC an address is a 32-bit value. As such, labels are 32-bit values when they are used in assembly language programs. PDF George M. Georgiou Brian Strader In the hello world example, line 7 contains the label "HW." The program uses this label to reference the "Hello World!" string. Labels are also used for branching, which are similar to labels and goto's in C++. Labels are optional and if an instruction does not have a label, usually empty space is left where one would be.
Assembly Language Syntax by Valvano Examples. Assembly Language Syntax Programs written in assembly language consist of a sequence of source statements. Each source statement consists of a sequence of ASCII characters ending with a carriage return. Each source statement may include up to four fields: a label, an operation (instruction mnemonic or assembler directive), an operand ... Embedded Systems - Assembly Language - Tutorialspoint The names used for labels in assembly language programming consist of alphabetic letters in both uppercase and lowercase, number 0 through 9, and special characters such as question mark (?), period (.), at the rate @, underscore (_), and dollar ($). The first character should be in alphabetical character; it cannot be a number. PDF Assembly Language NOW, Under21, R2D2, and C3PO are all examples of possible LC-3bassembly language labels. There are two reasons for explicitly referring to a memory location. 1. The location contains the target of a branch instruction (for example, AGAIN in line 0E). 2. PDF Chapter 2 HCS12 Assembly Language - TTU CAE Network A line of an assembly program Label field ... 2.1 Assembly language program structure 2.2 Arithmetic instructions 2.3 Branch and loop instructions ... Example: Write a program to add two 4-byte numbers that are stored at $1000-$1003 and $1004-$1007, and store the sum at $1010-$1013.
Assembly - Conditions Assembly - Conditions, Conditional execution in assembly language is accomplished by several looping and branching instructions. These instructions can change the flow of control in a. ... JMP label Example. The following code snippet illustrates the JMP instruction − ... LC3 Assembly Language.ipynb - Bryn Mawr College LC3 Assembly Language¶. More abstract, with additional powers: Labels; Instruction and Register names; Assembler Directives.ORIG - location to store code/data.END - end assembly process.FILL - Value for this memory location.BLKW - Block of Words.STRINGZ - Initialize memory with ASCII values, 0-terminated; Shorthand for using decimal and hexadecimal numbers Assembly - Label | Assembly | Datacadamia - Data and Co Grammar - Label in Assembly. A label is a name given to an addresses. Without the programmer would be required to manually calculate them. It's used to identify a target address storing: a instruction for a branch instruction (ie the value of the target address is executed) data (ie the value of target address is used as data in an operation) Assembly Language Programming • ECEn 323: Computer ... Assembly language is more readable than the binary machine code and is easier to edit and manipulate. The purpose of the "assembler" is to translate the text assembly language file written by a human into binary machine code executed by the processor (See section 2.12 in the textbook). This process is tedious and best left to a computer.
Jumping to Labels in Inline Assembly | Microsoft Docs Labels defined in __asm blocks are not case sensitive; both goto statements and assembly instructions can refer to those labels without regard to case. C and C++ labels are case sensitive only when used by goto statements. Assembly instructions can jump to a C or C++ label without regard to case. The following code shows all the permutations:
What are Labels in assembly language? - Quora The label is in fact a shorthand for skipping the manual calculation of the number of bytes to add to or subtract from the index pointer, for jump to label means just setting the new place in the memory the execution should continue at, ip+ or - some value.
PDF Graded ARM assembly language Examples - AlanClements Graded ARM assembly language Examples These examples have been created to help students with the basics of Keil's ARM development system. I am providing a series of examples that demonstrate the ARM's instruction set. These begin with very basic examples of addition. If any reader has difficulties with this material or can suggest
8086 assembly language loop instruction - 4Beginner.com 8086 assembly language loop instruction. a loop instruction is used to loop a group of instructions until the condition satisfies, i.e., CX = 0. To get the loop instruction to work first you have to define a label, set the value in cx which would be the number of times the loop should execute.
labels in assembly language examples In example-1, when first time program runs, A gets value 25, and then when R2 decrements from 10 to 1, output is 275 instead of 250. procedures or labels. Provide examples of three different instruction mnemonics. 10/7/2012 GC03 Mips Code Examples Conditional Branch Instructions - using labels calculating offsets is difficult - use a label instead!
SECTION V-10: Rules for Labels in Assembly Language ... The names used for labels in assembly language programming consist of alphabetic letters in both upper and lower case, the digits 0 through 9, and the special characters question mark (?), period (.), at (@), underline (_), and a dollar sign ($). The first character of the label must be an alphabetic character.
Labels and Mainframe Assembler Macro Usage Macro with Branch & Labels The following examples will show how to use Macro Files that will generate code with Branch Instructions and unique labels. Branch with a Specified Label Using explicit names in the mainline code creates code that is simple and easy to understand.
Assembly language - Wikipedia Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an assembler.
PDF Chapter 3 Assembly Language Fundamentals Assembly Language Fundamentals 3.1 Basic Elements of Assembly Language 51 3.1.1 Integer Constants 52 3.1.2 Integer Expressions 52 ... • memory (data label): ex. count Examples of assembly language instructions having varying numbers of operands • No operands stc ; set Carry flag • One operand
Example of Assembly - University of Aberdeen Example of Assembly. Source code format. A typical line in assembly language programme might be as follows: LOOP: MOV.B r0, #80 ;initialise counter. This line will be assembled into a single instruction (in this case 11 0000 1000 0000 in binary, or 3080); the assembly language and the machine code correspond to each other.
PDF Lecture 5 Basic Elements of Assembly Language Data Labels : a data label identifies the location of a variable, providing a convenient way to reference the variable in code. The following, for example, defines a variable named count: count DWORD 100 The assembler assigns a numeric address to each label. It is possible to define multiple data items following a label.
Labels (x86 Assembly Language Reference Manual) When a numeric label is used as a reference (as an instruction operand, for example), the suffixes b ("backward") or f ("forward") should be added to the numeric label. For numeric label N, the reference Nb refers to the nearest label N defined before the reference, and the reference Nf refers to the nearest label N defined after the reference.
8051 - "Label" in Assembly language - Stack Overflow Label is not bypassed. If you take a look at working of a loop then u will see that first DJNZ decrements the value of register then if the result is non zero it executes the label. In 1st example, starting from above: 1) A gets zero, then. 2) R2 gets 10, then. 3) A gets 25, then. 4) DJNZ decrements the value of R2 making it 9 and since the ...
retro computing - How do labels execute in Assembly ... A label is just a name for a location in your program. Labels are only used during assembly and do not generate any code. They do not "contain" anything or "execute" in any way. A function in assembly typically starts with a label, so that you can refer to the function by its name instead of having to figure out the address yourself ...
Label (computer science) - Wikipedia In assembly language labels can be used anywhere an address can (for example, as the operand of a JMP or MOV instruction). Also in Pascal and its derived variations. Some languages, such as Fortran and BASIC, support numeric labels. Labels are also used to identify an entry point into a compiled sequence of statements (e.g., during debugging ).











Post a Comment for "39 labels in assembly language examples"