40 indexing using labels in dataframe
Tutorial: How to Index DataFrames in Pandas - Dataquest Label-based Dataframe Indexing As its name suggests, this approach implies selecting dataframe subsets based on the row and column labels. Let's explore four methods of label-based dataframe indexing: using the indexing operator [], attribute operator ., loc indexer, and at indexer. Using the Indexing Operator How to select subset of data with Index Labels? - tutorialspoint.com With.iloc attribute, pandas select only by position and work similarly to Python lists. The .loc attribute selects only by index label, which is similar to how Python dictionaries work. Select a Subset Of Data Using Index Labels with .loc[] The loc and iloc attributes are available on both Series and DataFrame
Indexing Dataframes. Indexing Dataframes in Pandas | by Vidya Menon ... loc Method: Using Single label:. Helps to specify which rows and/or columns we want .For rows, the label is the index value of that... List or Array of Labels:. What if we want multiple rows and/or columns instead of just one. Well, with using array of... Slice Object:. Boolean Array:. Last but not ...

Indexing using labels in dataframe
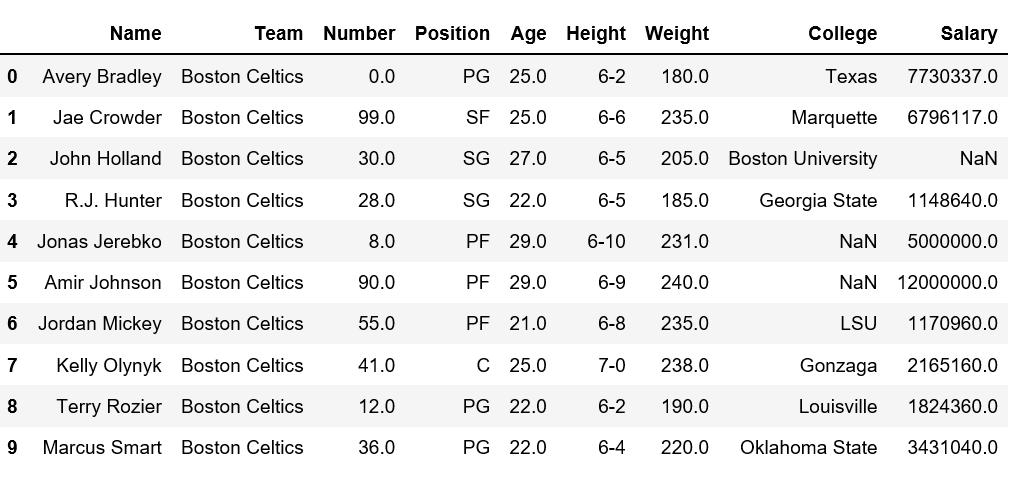
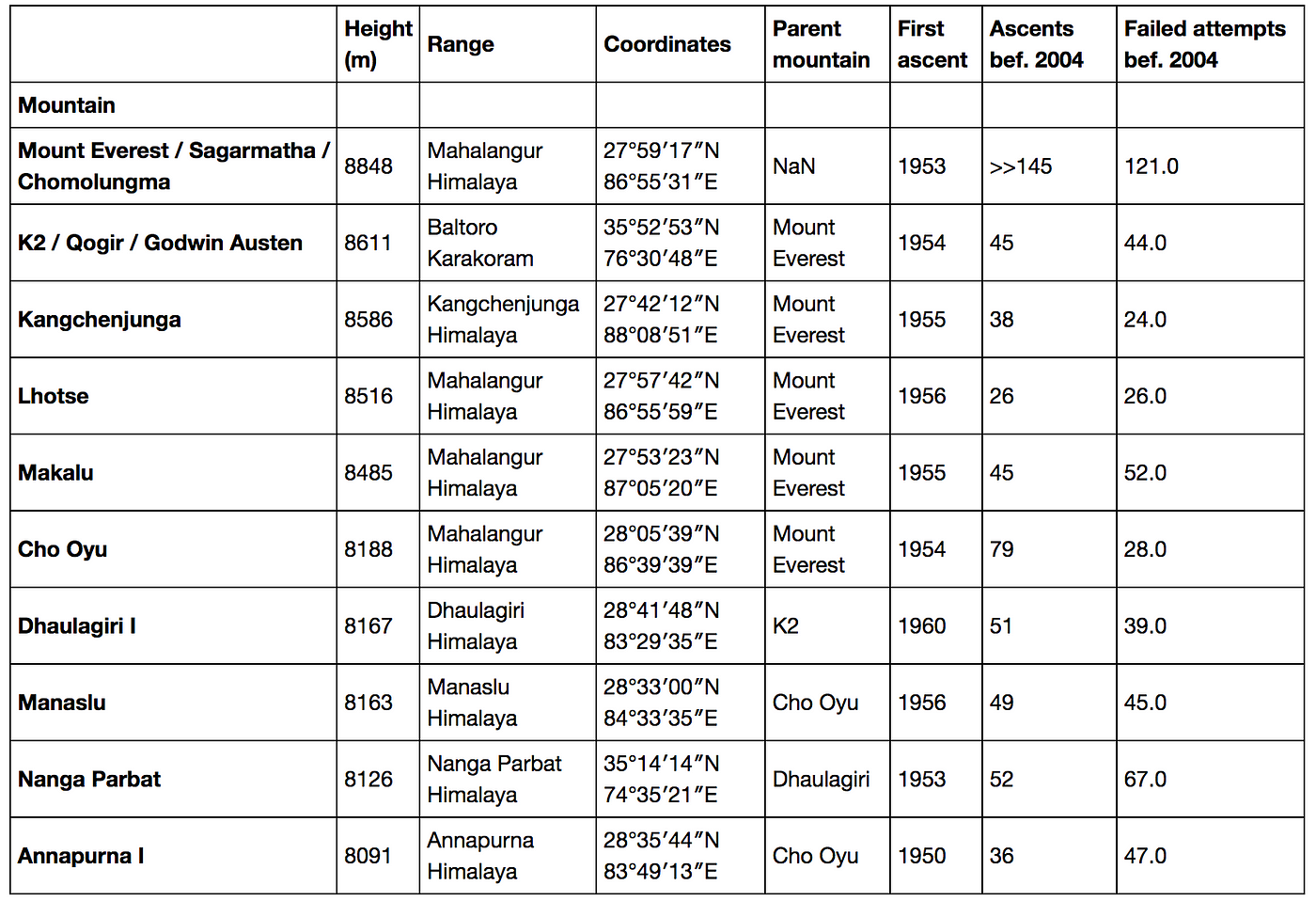
Label-based indexing to the Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks Indexing plays an important role in data frames. Sometimes we need to give a label-based "fancy indexing" to the Pandas Data frame. For this, we have a function in pandas known as pandas.DataFrame.lookup (). The concept of Fancy Indexing is simple which means, we have to pass an array of indices to access multiple array elements at once. Pandas DataFrame Indexing Streamlined - Table of Contents In pandas data frames, each row also has a name. By default, this label is just the row number. However, you can set one of your columns to be the index of your DataFrame, which means that its values will be used as row labels. We set the column 'name' as our index. It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on. To get subset of dataframe based on index of a label Question: I have a dataframe from yahoo finance This gives me df as, If I specify, I need a subset of df with row having indexes label "2021-04-23" rows of 2 days before the date row of 1 day after of date The important thing here is, we cannot calculate before & after using date strings as df may not have some dates but rows to be printed based on indexes.
Indexing using labels in dataframe. Pandas Select Rows by Index (Position/Label) Use pandas DataFrame.iloc[] & DataFrame.loc[] to select rows by integer Index and by row indices respectively. iloc[] operator can accept single index, multiple indexes from the list, indexes by a range, and many more. loc[] operator is explicitly used with labels that can accept single index labels, multiple index labels from the list, indexes by a range (between two indexes labels), and many ... Indexing and selecting data — pandas 2.0.0.dev0+615.ge7a5c9295f ... A single label, e.g. 5 or 'a' (Note that 5 is interpreted as a label of the index. This use is not an integer position along the index.). A list or array of labels ['a', 'b', 'c']. ... You may select rows from a DataFrame using a boolean vector the same length as the DataFrame's index (for example, something derived from one of the columns of ... pandas.DataFrame.set_index — pandas 1.5.1 documentation Set the DataFrame index (row labels) using one or more existing columns or arrays (of the correct length). The index can replace the existing index or expand on it. Parameters. keyslabel or array-like or list of labels/arrays. This parameter can be either a single column key, a single array of the same length as the calling DataFrame, or a list ... Pandas DataFrame Indexing: Set the Index of a Pandas Dataframe In this method, we can set the index of the Pandas DataFrame object using the pd.Index() and set_index() function. First, we will create a Python list then pass it to the pd.Index() function which returns the DataFrame index object. Then we pass the returned DataFrame index object to the set_index() function to set it as the new index of the DataFrame. Let's implement this through Python code.
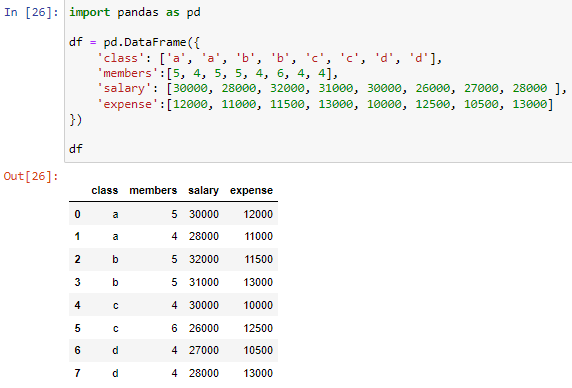
Indexing and Selecting Data with Pandas - GeeksforGeeks Pandas support four types of Multi-axes indexing they are: Dataframe. [ ] ; This function also known as indexing operator Dataframe.loc [ ] : This function is used for labels. Dataframe.iloc [ ] : This function is used for positions or integer based Dataframe.ix [] : This function is used for both label and integer based Select Rows & Columns by Name or Index in Pandas DataFrame using ... The . loc [] function selects the data by labels of rows or columns. It can select a subset of rows and columns. There are many ways to use this function. Example 1: Select a single row. Python3 import pandas as pd employees = [ ('Stuti', 28, 'Varanasi', 20000), ('Saumya', 32, 'Delhi', 25000), ('Aaditya', 25, 'Mumbai', 40000), Python Pandas: Get Index Label for a Value in a DataFrame I typically do the following using np.where: import numpy as np idx = df.index [np.where (df ['hair'] == 'blonde')] Which gives the expected result: Index ( [u'mary'], dtype='object') If you want the result in a list, you can use .tolist () method of index Share Follow answered Jun 14, 2017 at 15:28 FLab 6,816 3 34 63 Add a comment Your Answer How to drop rows in Pandas DataFrame by index labels? Rows can be removed using index label or column name using this method. Syntax: DataFrame.drop (labels=None, axis=0, index=None, columns=None, level=None, inplace=False, errors='raise') Parameters: labels: String or list of strings referring row or column name. axis: int or string value, 0 'index' for Rows and 1 'columns' for Columns.
Working With Specific Values In Pandas DataFrame - Data Courses This function of a pandas DataFrame is of high value as you can build an index using a specific column, (meaning: a label) that you want to use for managing and querying your data. For example, one can develop an index from a column of values and then use the attribute.loc to select data from pandas DataFrame based on a value found in the index. How to Get the Last Column of a Pandas Dataframe? 1. Fetching the last column by index : In case we are not aware of the last column name then we can always access the last column by its index, using the iloc property. Syntax: dataFrameName.iloc [:, -1] Note: Pandas dataframes support negative indexing which can be helpful when trying to access values from the end of an indexable object (like ... Indexing in Pandas Dataframe using Python | by Kaushik Katari | Towards ... Indexing using .loc method. If we use the .loc method, we have to pass the data using its Label name. Single Row To display a single row from the dataframe, we will mention the row's index name in the .loc method. The whole row information will display like this, Single Row information Multiple Rows Indexing and selecting data — pandas 1.5.1 documentation Indexing and selecting data #. The axis labeling information in pandas objects serves many purposes: Identifies data (i.e. provides metadata) using known indicators, important for analysis, visualization, and interactive console display. Enables automatic and explicit data alignment. Allows intuitive getting and setting of subsets of the data set.
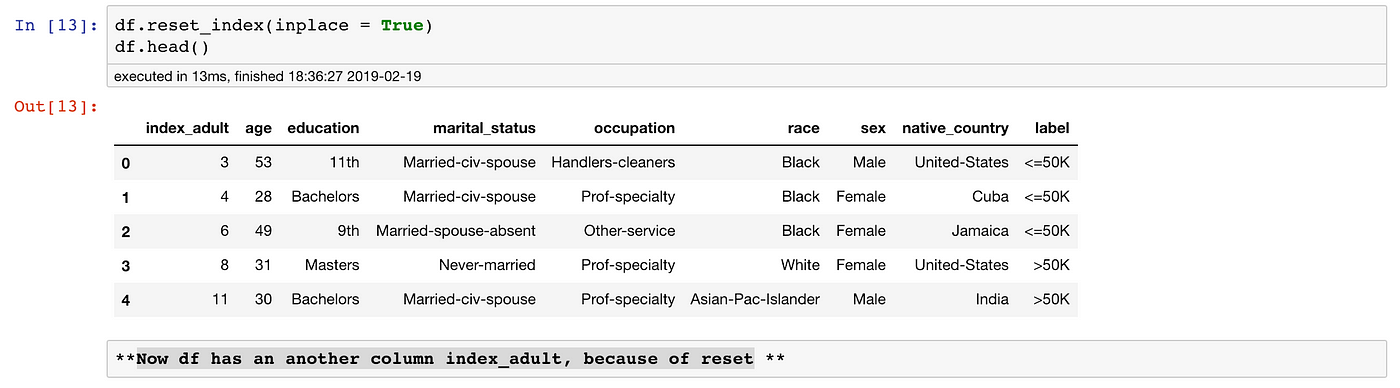
Pandas Dataframe Index in Python - PythonForBeginners.com When a dataframe is created, the rows of the dataframe are assigned indices starting from 0 till the number of rows minus one. However, we can create a custom index for a dataframe using the index attribute. To create a custom index in a pandas dataframe, we will assign a list of index labels to the index attribute of the dataframe.
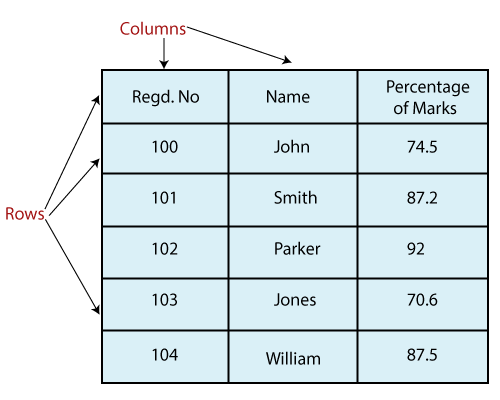
Pandas DataFrame Indexing Explained: from .loc to .iloc and beyond Indexing can be described as selecting values from specific rows and columns in a dataframe. The row labels (the dataframe index) can be integer or string values, the column labels are usually strings. By indexing, we can be very particular about the selections we make, zooming in on the exact data that we need.
Get Rows using Datetime Index in Pandas - Data Science Parichay To get Pandas dataframe's rows using a datetime index, the syntax will be-. row = df.loc[date] Here, df — The Pandas DataFrame object. df.loc [] — A property of Pandas DataFrame to get rows using their row labels. In the above code, we have a dataframe df with datetime indices. We pass a date to df.loc [] to fetch the required row using ...
Boolean Indexing in Pandas - tutorialspoint.com Practical Data Science using Python. Boolean indexing helps us to select the data from the DataFrames using a boolean vector. We need a DataFrame with a boolean index to use the boolean indexing. Let's see how to achieve the boolean indexing. Create a dictionary of data. Convert it into a DataFrame object with a boolean index as a vector.
Boolean Indexing in Pandas - GeeksforGeeks In boolean indexing, we will select subsets of data based on the actual values of the data in the DataFrame and not on their row/column labels or integer locations. In boolean indexing, we use a boolean vector to filter the data. Boolean indexing is a type of indexing that uses actual values of the data in the DataFrame.
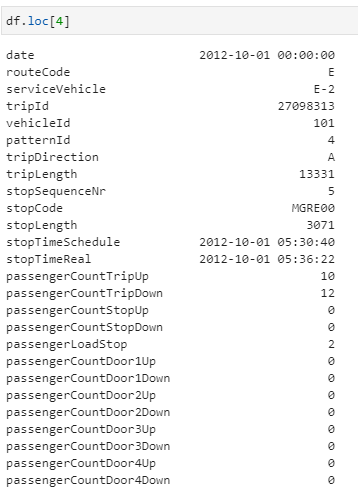
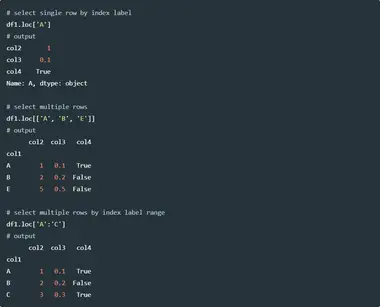
Get Rows by their Index and Labels - Data Science Parichay You can use the pandas dataframe loc property to access one or more rows of a dataframe by their row labels. The loc property in a pandas dataframe lets you access rows and/or columns using their respective labels. The following is the syntax. # select row with label l df.loc[l] # select rows with labels l, m, and n df.loc[ [l, m, n]] Examples
Indexing into Dask DataFrames — Dask documentation Label-based Indexing¶ Just like Pandas, Dask DataFrame supports label-based indexing with the .loc accessor for selecting rows or columns, and __getitem__ (square brackets) for selecting just columns. Note. To select rows, the DataFrame's divisions must be known (see Internal Design and Dask DataFrames Best Practices for more information.)
Pandas DataFrame Indexing - KDnuggets Use .loc[] for label-based indexing; Use .iloc[] for position-based indexing, and; Explicitly designate both the rows and the columns even if it's with a colon. This set of guidelines will give you a consistent and straightforwardly interpretable way to pull the data that you need from a pandas DataFrame. Good luck with your data munging!
To get subset of dataframe based on index of a label Question: I have a dataframe from yahoo finance This gives me df as, If I specify, I need a subset of df with row having indexes label "2021-04-23" rows of 2 days before the date row of 1 day after of date The important thing here is, we cannot calculate before & after using date strings as df may not have some dates but rows to be printed based on indexes.
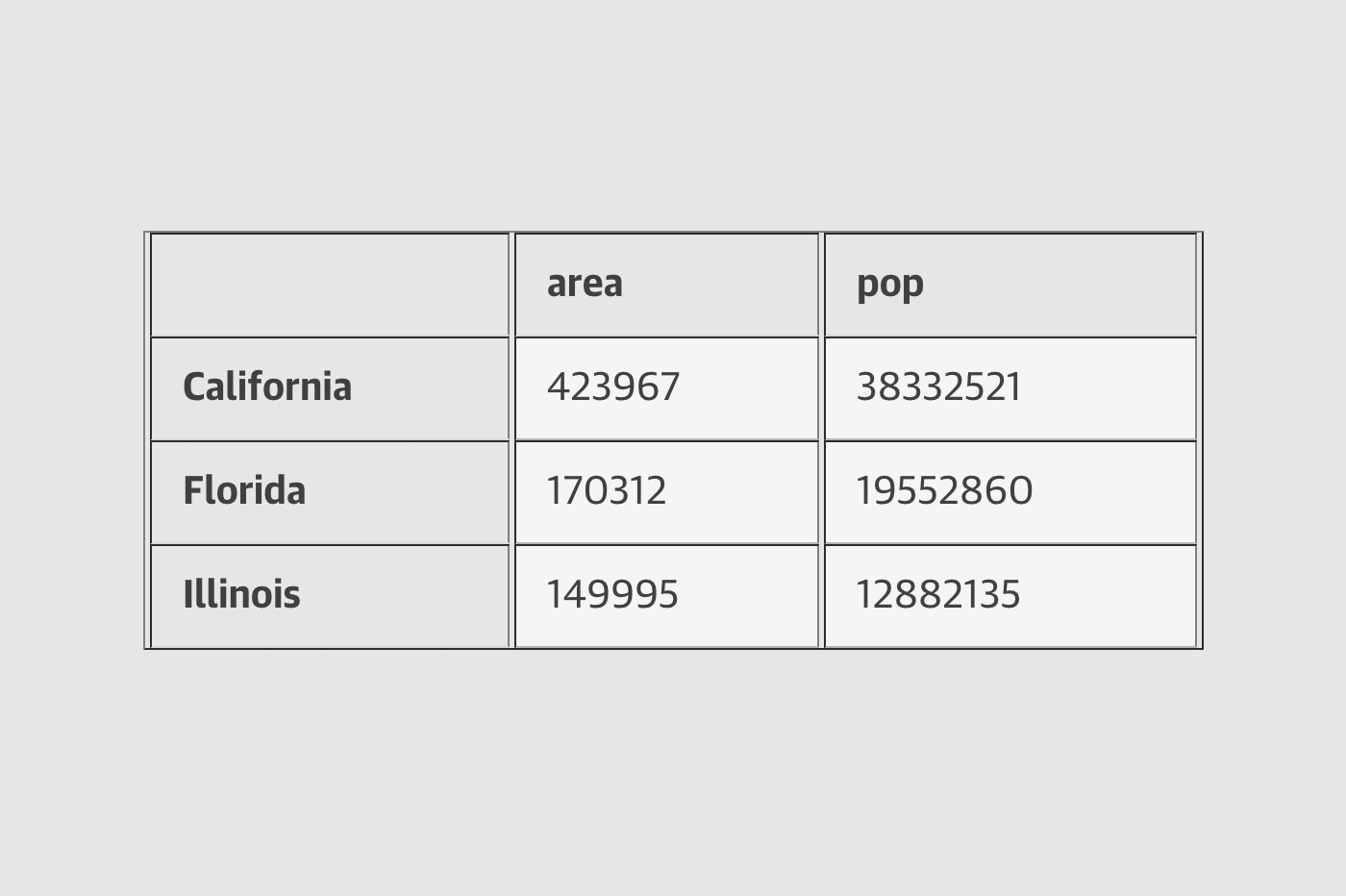
Pandas DataFrame Indexing Streamlined - Table of Contents In pandas data frames, each row also has a name. By default, this label is just the row number. However, you can set one of your columns to be the index of your DataFrame, which means that its values will be used as row labels. We set the column 'name' as our index. It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on.
Label-based indexing to the Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks Indexing plays an important role in data frames. Sometimes we need to give a label-based "fancy indexing" to the Pandas Data frame. For this, we have a function in pandas known as pandas.DataFrame.lookup (). The concept of Fancy Indexing is simple which means, we have to pass an array of indices to access multiple array elements at once.



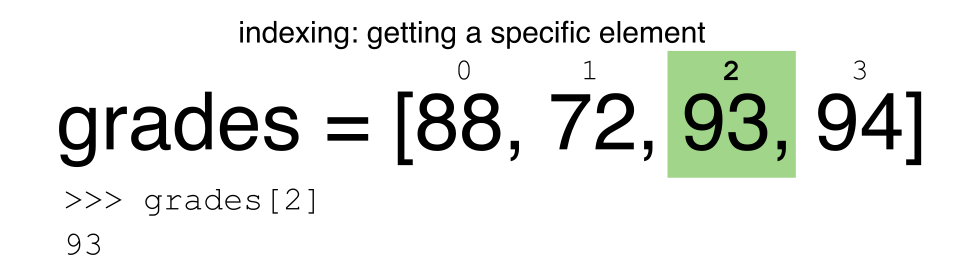











-Feb-14-2022-02-23-55-63-PM.png?width=650&name=Pandas%20Indexing%20(V4)-Feb-14-2022-02-23-55-63-PM.png)












Post a Comment for "40 indexing using labels in dataframe"